John’s mobile rang while he was about to compose a work e-mail. Happily vibrating on the surface of his desk as if it was making almost a dance to the rhythm of his ringtone.
John glanced at the display, it showed an unknown caller ID.
“Oh, another sales call,” John thought to himself, but for whatever reason, he felt like answering it. Maybe it was just a sign of his procrastination and the fact that he didn’t really want to write that e-mail, so any excuse to push it back was acceptable. But as he was about to answer, John’s hand stopped mid-air hesitating for a second and then he pressed the red button rejecting the call.
Instantly forgetting about it, John clicked on the new message and started to type. He didn’t manage to write maybe a sentence when he was again interrupted by the same ringtone and unknown caller ID. This time John decided to answer.
“Hello?” asked John
“Hello”, said the person on the other side. “Am I talking to John Bridtower?”
“Eeerr yes? What is this about?”
“My name is Jake I am calling from the PayPal fraud department, we have detected a £2000 transfer request to leave your account in the next few minutes, due to international regulations we are unable to withhold the funds any longer. I was trying to reach you earlier but the number we had was incorrect. However, I was lucky and found this number. Just to confirm am I talking to John Bridgetower?”
John was getting very nervous, what the man was saying didn’t make any sense. Who, how and why? Was running through John’s head. Was that payment for something he bought? When was the last time he bought something? Where? Was it on Amazon? Thought run through his head at a crazy speed.
“Mr John, are you able to confirm if is that you?”
“Eee, yes, my name is John Bridgetown. But I don’t know anything about the transfer. Can you stop it?”
“Yes, Mr John, however, for the GDPR reason I have to confirm that I am really talking to the account holder before I can do anything. Would that be ok?”
“Yes, of course, yes” replied John.
“Ok, Mr John I will send you a verification number, which you will get on your mobile phone, please read this to me back. ok but please be prompt as the code is valid only for 30-60 seconds and we are almost out of time for me to stop the transfer.”
“Yes, I will”
John’s mobile buzzed as the SMS arrived, there was a string of text and a 6-digit number. John quickly read the number out loud to his phone.
“Did you get it?” asked John.
A few seconds went, which felt much longer, and finally, the voice on the other side answered:
“Yes, Mr John, I can confirm it is really you. Thank you for working with the fraud department at Paypal. I can ensure you I have managed to stop the transfer. All your money is now safe. I hope you will have a wonderful day. Oh yes, can you please for security reasons not log on to your account for at least 2-3 hours while we try to catch whoever was trying to move money out of your account? Would that be ok?”
“Yes, please, are you sure my money is safe?”
“Oh yes, Mr John I can see your balance is restored, so all good. Have a great rest of the afternoon.”
“Morning actually, it is morning” John replied.
There was silence on the other side and John saw he was looking at the disconnected screen.
“Phew! That was stressful and a close call. I wonder how they manage to access my account” thought John to himself.
He decided he needed his caffeine hit, so went downstairs to make a nice cuppa of coffee.
By the time he was back at his desk, his phone had dozen of notifications from his bank about outgoing transactions from all sorts of places, £500 here, £1200 there. John’s heart stopped, and his hands froze, trying to process what was happening in front of his eyes.
How? What is happening? Panic was spreading like wildfire.
John opened his bank account with more than £20K missing, and more transactions were being processed. With shaking hands, John tries to open his Paypal account, but for whatever reason, his password is not accepted.
John tries again, and again. It is the same password he used everywhere. He is typing it correctly! What is happening!!!?
The end.
Be Aware! Thread Actors Coming Your Way!
We hope you enjoyed our small example of how Thread Actors try to outsmart users and Two-Factor Authentication. What we have shown you above is a pretty real example. Every security solution is as strong as its weakest link. People who try to steal your money or access confidential information are smart, and what is more important they try attacking you unlimited times but they only need to be successful once.
An average user needs to be smart enough to recognize phishing attempts and know how to react. The technology only can go as far but without the user being aware of how to use it, well we need you to protect yourself.
Phishing attempts will only increase in popularity as times go as they offer a massive payout for every successful attack. Any online account is a potential target, your email address is a way to send attackers in your direction. Just type your email address in google and see how many results it brings.
Evolution of Security Solutions
Technology gurus are trying to improve our security constantly and each time we learn something new.
First, we used just a username and password, as it turned out people are very bad at creating complex passwords and frequently use the same password all over the place.
Solution? Password manager which can create super complex passwords for our online accounts.
Then users were tired of typing long complex passwords so we needed another solution such as Facial Recognition or fingerprint reader. That definitely helped as mighty Apple introduced Facial Recognition known as Apple FaceID.
Then the Thread Actors found a good way to access large databases of passwords by simply hacking Online Providers such as Google, Yahoo, Facebook and more. That led to more attacks.
A solution? We needed another password-like code that even user does not know until they are ready to use it.
How would you protect, for example, a Bank Account? Well, how about we send a text message with a code? That worked, at least for a while. Because, Tread Actors, yet again, figured out how to overcome this.
The solution? An App that will do the same job! The clear advantage is that Thread Actor does not know what app the user uses and the security of such an app is much harder to break.
Problem solved? Right? Well, almost. The above fun story presented an ingenious way that Tread Actors uses to persuade users to disclose the code to them, overcoming yet another security layer.
Technology will constantly improve and we can add more and more layers of security, but if we are missing a crucial component which is education, this is just a never-ending story: IT professionals add another layer of security to our devices and Thread Actors find another way around it. Rinse, repeat right?
We should highlight the importance of the missing ingredients – the education on Cyber Security for End Users. Everyone can be hacked, even the professionals like us with many years of experience, but if we keep on educating ourselves, together we can create a much harder barrier to break through.
If you would like to find out more about how a proper password should look CLICK HERE
What is Two-Factor Authentication or Multi-factor authentication (MFA)?
Before we jump to explain what tactics are used by Thread Actors let’s remind ourselves what is actually 2FA/MFA.
2FA is two-factor authentication which is part of MFA or Multi-factor authentication.
2FA consist of a login, password and a code that is generated on demand by an authorised user, MFA is a larger system that incorporates 2FA. In MFA access to the data is from multiple sources, such as passwords, a code that is generated on demand, and biometric sensor data such as FaceID or fingerprint such as TouchID, but it can extend to more advanced technologies as well.
On the end-user device, you will see this as an App. Before you log on to one of your online accounts you will be required to provide the code using the App. This way MFA adds extra layers of protection against unauthorized access. However, like any security measure, MFA is not foolproof, and there are ways for attackers to outsmart it as we have explained above.
So let’s explore some of the most common ways attackers can bypass MFA and what you can do to protect yourself.

6 Ways How Attackers Are Bypassing Multi-Factor Authentication
1. Social Engineering
Social engineering is the art of manipulating people into divulging confidential information. Attackers use social engineering tactics to trick users into providing access to their accounts. For example, an attacker may call or email a user and impersonate a legitimate company, such as a bank or a technology company, to request the user’s login credentials or MFA token. In some cases, attackers may create fake login pages that look like the real thing to trick users into entering their login credentials.
To protect yourself from social engineering attacks, you should always verify the authenticity of any requests to provide sensitive information or requests to gain access to any of your online accounts. This can be achieved by checking if the domain name is spelt correctly, ensuring that you can see the full name, as the hidden parts of the long domain names can potentially hide misspelt names which would suggest this is not a legitimate website.
If in doubt, it is much better to open a new browser window and type the address instead of clicking on the suspicious links. On Mobile devices, you should use a dedicated App.
You should also be cautious of unsolicited calls or emails, particularly if they ask for sensitive information or financial transfers. Additionally, be mindful, if someone asks you a Security Question, is it really safe to provide an answer to someone who just called you? How do you know, they are who they say they are?
If you have any uncertainty, please hang up the call and dial the provider directly from a number you already have, not from the email you just received from them or don’t dial back the number that called you.
Additionally, it is prudent to make the call from another phone. Why? Because UK landlines terminate the call when the person who initiated the call hangs up. If the recipient hangs up, that does not end the call. Therefore, even if you hang up and dial a new number, let’s say you might be calling your bank after a suspicious phone call you just received, you never know who will be on the other side. Is it really the bank or hacker that was waiting on the line, hearing you dial the number and played along to the new scenario?
Using another phone helps to prevent this issue.
2. Consent Phishing
Consent phishing is a type of attack that exploits the trust which users have in legitimate websites or applications. In a consent phishing attack, the attacker creates a fake website or application that looks just like a real one and once the user types his/hers login and password details, hackers use it to log in to a genuine website and steal sensitive data or launch further attacks.
To protect yourself from consent phishing attacks, you should always verify the authenticity of the website or application before granting access to your account.
As we have mentioned above it is a good idea, to use your bookmark, type a full address or use a search engine to access the desired website instead of using links from Suspicious Emails.
You should also use trusted antivirus software which can detect and block fake websites or applications and be aware of malicious software.
3. Brute Force
Brute force is a type of attack which involves trying every possible combination of characters until the correct one is found. These attacks are often used to guess passwords, but they can also be used to guess MFA tokens
A prime illustration of this was a brute force attack in which a White Hat Hacker (ethical security hacker) demonstrated how effortless it was to gain control of any Instagram account.
At the time Instagram had a flaw with the password reset policy.
The security researchers discovered that Instagram asks for a numeric PIN which they email to the owner of the account. This was sufficient for the ethical hacker to utilise the power of cloud servers and bombard Instagram with requests to log on with any possible 6-digit combination and finally gain access to the account. Basically, the white hacker tried every possible 6-digit combination in a space of a few minutes until he found the correct one, which normally only a user should have. The same method could grant him access to any account.
To protect yourself from brute force attacks, you should use complex passwords that include letters, numbers, and symbols. You should also avoid using the same password for multiple accounts and update your passwords regularly. Additionally, you should restrict access to your accounts and monitor login attempts to detect suspicious activity.
4. Exploiting Generated Tokens
MFA tokens are generated by a third-party provider and are designed to be unique and difficult to guess. However, in some cases, attackers can exploit the way these tokens are generated to gain access to a user’s account.
To protect yourself from attacks that exploit generated tokens, you should use adaptive multi-factor authentication (AMFA). AMFA uses machine learning algorithms to analyze user behaviour and adapt the authentication process accordingly. This can help detect and block attacks that exploit generated tokens.
5. Session Hijacking
Session hijacking is an attack method that entails stealing a user’s session ID. The session ID is utilized to recognize the user’s ongoing session on a website or app. If the attacker gains access to the session ID, they can seize control of the user’s session and acquire entry to their account.
To protect yourself from session hijacking, you should always use a secure connection when accessing websites or applications. As you can see the end user machine is a device that can be used to gain access to a corporate network. In such a situation, Zero Trust Security Model will be beneficial due to 2 main components.
1st – every device has only a minimal permissions level required to complete the task and
2nd – if the end-user device is not compliant the permission to access the system is revoked.
In order to stay compliant users’ computers should use trusted antivirus software that can detect and block session hijacking attempts and have a fully patched Operating System and all updates installed.
To learn what Zero Trust Security is CLICK HERE
6. SIM Hacking
SIM hacking is a type of attack that involves “stealing” a user’s SIM card. All that Hackers have to do is to call a person’s mobile provider, like O2 or EE, and convince them that they are the owner of the number and ask them to move the number to a brand new SIM, which of course is in their possession. When the attacker has access to the SIM card, they can use it to intercept SMS-based MFA codes and gain access to the user’s accounts.
This way the owner of the number doesn’t know what is happening until their SIM suddenly is deactivated, and their number is stolen together with savings from their bank account.
SIM hacking led to a massive spike in fraud, and many bank accounts were emptied.
To protect yourself from SIM hacking, you should contact your mobile provider and request that they add a PIN or password to your account. This can help prevent attackers from transferring your phone number to a different SIM card. However, a much better alternative is to stop using your mobile phone as a Multifactor Authentication and instead use one of the authenticator Apps or even better use a security hardware key, that does not rely on SMS codes.
How to stay secure and one step ahead of Thread Actors?
Use Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication
As mentioned earlier, using adaptive multi-factor authentication (AMFA) is a great way to protect yourself from attacks that exploit generated tokens. AMFA uses machine learning algorithms to analyze user behaviour and adapt the authentication process accordingly. This can help detect and block attacks that exploit generated tokens, as well as other types of attacks.
Use Complex Passwords, Restrict Access, and Monitor Logon Attempts
Using complex passwords that include letters, numbers, and symbols is essential for protecting your accounts. You should also avoid using the same password for multiple accounts and update your passwords regularly.
Additionally, you should restrict access to your accounts and monitor login attempts to detect suspicious activity.
We appreciate that it’s easier said than done because we have hundreds, if not thousands, of online services to keep track of for unsuccessful login attempts. This is a challenging task. Fortunately, this is when technology comes to help.
First of all, many Online Services will send you an email when certain changes happen to your accounts such as a password reset, or a change of the email address. Another good tool to have is Password Manager which can monitor any data leaks, or suggest replacement passwords if they detect your passwords are weak. Not to mention it will generate a complex password for each website you use.
Check out our blog for more tips on how not to get hacked- CLICK HERE
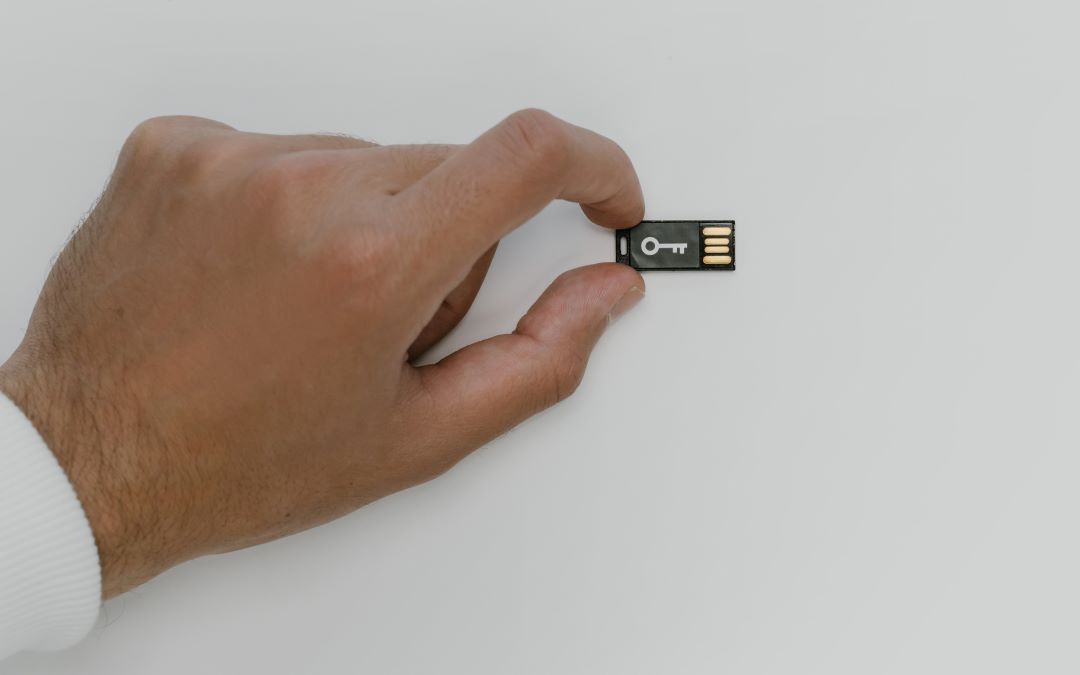
Hardware Keys Are a Solution
Hardware keys are physical devices that are used for two-factor authentication (2FA) to protect your accounts and devices. These keys are designed to work in tandem with your username and password to ensure that only authorized users can access your accounts and data. They come in various forms, such as USB sticks, NFC cards, or Bluetooth devices.
Hardware keys offer several advantages over traditional password-based authentication methods. They are much harder to attack than passwords, which can be easily compromised through brute-force attacks, social engineering, or phishing. Security keys generate a unique code every time they are used, making it nearly impossible for attackers to predict or replicate the code. Thanks to hardware keys we can remove the weak links in our security systems such as SMS Verification.
To find out more about why we should all be using Security Hardware Keys- CLICK HERE
Conclusion
A multi-factor authentication/ 2FA/ AMFA is an essential tool for securing online accounts and data, but it is not foolproof. Attackers can use a variety of tactics to bypass MFA, such as social engineering, consent phishing, brute force, exploiting generated tokens, session hijacking, and SIM hacking. However, by using adaptive multi-factor authentication, complex passwords, restricting access, monitoring login attempts, and using hardware keys, you can significantly reduce the risk of a successful attack.
Implementing just half of the recommendations mentioned above can make a substantial difference in combating cybercrime and provide you with peace of mind.
How Operum.Tech Can Help?
At Operum.Tech, we offer a range of IT security services to help protect your business from cyber threats. Our team of experts can work with you to develop a comprehensive security strategy that includes MFA, password management, and other best practices. We can also provide training and support for your employees to help them stay safe and secure online.

In addition, we can help you implement hardware keys and other advanced security measures to protect your accounts and data. We stay up to date with the latest trends and threats in the IT security industry, and we use this knowledge to provide the best possible service to our clients.
One of our main advantages is that we are consistent and passionate about what we do. Therefore our approach is not patchy as every day we learn, work and gather new techniques to protect our customers.
If you want help from a team that is passionate about IT and IT security please talk to us by clicking below the Contact Us button or just simply call us 🙂
Sign up below to join the Operum newsletter